Published
- 2 min read
TLS testing on CI pipeline
CI unit/intergration test should mimic the same behaviour on production
Situation
- Your production database is TLS enabled
- Unit test must ensure the same TLS behaviour, eg: unit test on a Postgres docker image
- Use a dev database: costly (must always be up running) and have to erase entirely after pipeline finish
- Spawn a new database with docker
Objective
- Create an script that can access both a Postgres docker image (dev) and a RDS database (prod)
- Creating a CA chain that can work with both prod and dev
Prerequisites about SSL/TLS
** Definitions and acronyms **
- SSL vs TLS: these 2 are almost the same and currently used interchangeably
- Certificate Authority (CA): A unit that stands in the central to verify cryptographic keys
- Self-signed Certificate: when using self-signed certificate, you/your company stands as CA and generate certs to use internally
** The 4 keys/certs **
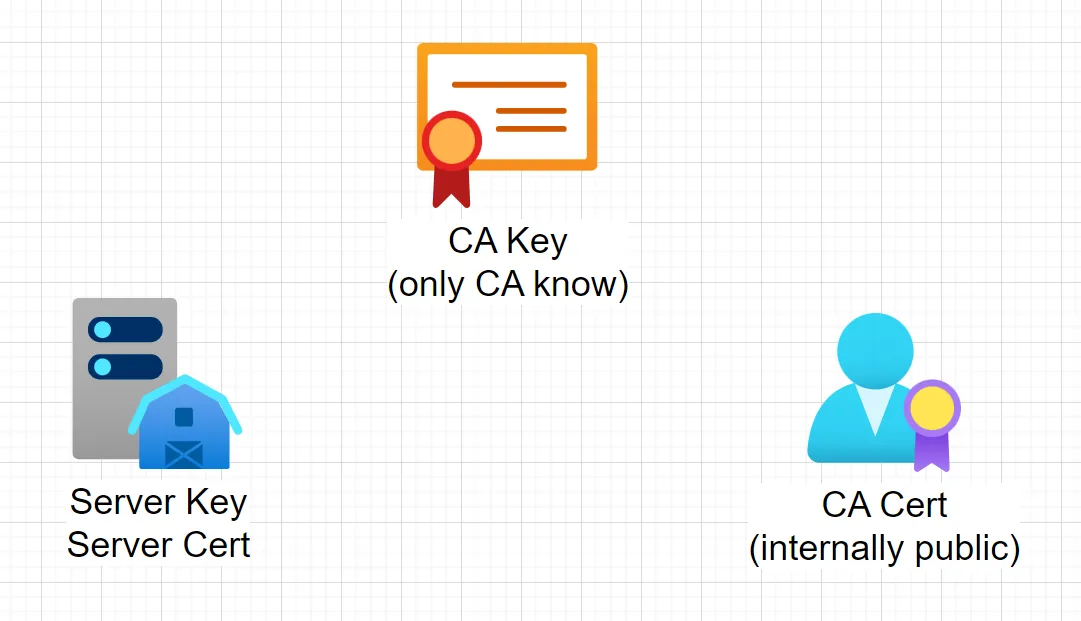
- CA key: secret key that CA holds
- CA cert: internally public key
- Server key + Server cert: secret key that encrypted server holds, generated from the CA key
Generating keys
- First thing first: root CA key
openssl genrsa -out ca.key 2048
- CA public cert
openssl req -x509 -new -nodes -key ca.key -days 365 -out cacert.pem -subj "/CN=example.com"
- Server key: simply another one just like the root CA key
openssl genrsa -out my.key 2048
- Generate a certficate signing request (CSR) with server key
openssl req -new -key my.key -out my.csr -subj "/CN=localhost"
- Last step: server cert
openssl x509 -req -in my.csr -CA cacert.pem -CAkey ca.key -days 365 -out cert.pem
TLS enabled Postgres image
For both Linux and Windows usage, we build a new image. Linux users can modify local keys permission then use it directly
FROM postgres:16.1
# On Windows root will own the files, and they will have permissions 755
COPY my.key /var/lib/postgresql/server.key
COPY cert.pem /var/lib/postgresql/server.crt
# update the privileges on the .key, no need to touch the .crt
RUN chmod 600 /var/lib/postgresql/server.key
RUN chown postgres:postgres /var/lib/postgresql/server.key
** Docker compose file for convenience **
version: '3.5'
services:
database:
image: my-postgres
build: .
ports:
- 5432:5432
environment:
# Default user is postgres
# Default database is postgres
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: password
command: -c ssl=on -c ssl_cert_file=/var/lib/postgresql/server.crt -c ssl_key_file=/var/lib/postgresql/server.key
Now go ahead spin up your Postgres with TLS enabled
docker-compose up -d
Client side
** A NodeJS script to verify the encrypted connection **
// index.js
const { Client } = require('pg')
const config = {
connectionString: 'postgres://postgres:password@localhost:5432/postgres?sslmode=require',
}
const client = new Client(config);
(async function () {
await client.connect()
console.log('Secure connection established!!!')
})()
Set NodeJS env to use our CA cert
set NODE_EXTRA_CA_CERTS=cacert.pem
Firing your connection test!!!
node index.js